В настоящем обзоре преимущественно проанализированы данные рандомизированных, контролированных исследований АА при лечении МС, которые имеют наибольшую доказательную ценность. На эти данные врачу следует опираться, прежде всего, при выборе той или иной терапии. Эффективность и переносимость АА определялась в сравнении как с плацебо, так и с классическими нейролептиками. Анализировались результаты монотерапии АА, или их сочетания с нормотимиками.
Наибольшее число слепых сравнительных плацебо-контролируемых исследований с большими выборками больных было проведено с применением ОЛЗ. Они показали его достаточную клиническую эффективность, однако процент выбывших из исследования больных (до 40 %) достаточно высок для того, чтобы дать однозначную положительную оценку переносимости препарата. Комбинированная терапия ОЛЗ в сочетании с нормотимиками оказалась наиболее эффективной при купировании МС. Важным преимуществом ОЛЗ является возможность в/м введения препарата с быстрым контролем психомоторного возбуждения. Однако главным побочным эффектом и недостатком терапии ОЛЗ было быстрое увеличение веса тела (более 1,5-2,0 кг за три недели терапии), отмечались также сонливость, головокружение, сухость во рту.
Плацебо-контролируемые исследования РИС также показали, что препарат достоверно превосходит плацебо и сопоставим по антиманиакальной эффективности, но вызывает дозозависимые экстрапирамидные побочные эффекты и гиперпролактинемию. Комбинированная терапия РИС с карбамазепином оказалась недостаточно эффективной из-за снижения концентрации рисперидона в крови в 1,5-2 раза вследствие фармакокинетического взаимодействия препаратов.
Данные рандомизированных контролированных исследований доказали также эффективность КВТ при купировании МС. Во всех исследованиях отмечался хороший профиль переносимости кветиапина, отсутствие экстрапирамидных побочных эффектов и гиперпролактинемии, что является важным преимуществом при назначении препарата у больных БАР.
Несколько слепых контролированных исследований зипрасидона и арипипразола также дали обнадеживающие результаты как в отношении антиманиакальной эффективности, так и хорошей переносимости этих препаратов у больных БАР.
Данные, полученные при использовании азенапина, нуждаются в подтверждении в дальнейших исследованиях на более многочисленных выборках больных.
Таким образом, результаты рандомизированных контролируемых исследований показывают, что АА примерно были сопоставимы по силе антиманиакального действия. У половины больных при лечении АА наблюдалась редукция маниакальной симптоматики по шкале YMRS более чем на 50 % после 3 недель терапии. В этих условиях при выборе терапии на первый план выступают быстрота достижения эффекта, определяющаяся во многом наличием лекарственных форм препарата для парентерального введения. Эффективность и безопасность АА делают их средствами предпочтительного выбора при купировании МС по сравнению с классическими нейролептиками и даже нормотимиками. Анализ высоко доказательных исследований АА при купировании МС показывает, что в виде монотерапии они не уступают традиционным схемам лечения, а в сочетании с нормотимиками в ряде случаев позволяют добиться большего успеха. Главным преимуществом терапии АА является их более высокая переносимость с практически полным отсутствием экстрапирамидных побочных эффектов. Известно, что больные БАР особенно чувствительны к развитию экстрапирамидной симптоматики и гиперпролактинемии (Ahlfors U., 1981; KaneJ., 2004), что необходимо учитывать при выборе антиманиакальной терапии.
Следует отметить, что несмотря на увеличение числа рандомизированных исследований, направленных на оценку эффективности препаратов при МС, их количество все еще остается меньшим, по сравнению с такими же исследованиями при шизофрении или депрессивном расстройстве (Sachs G., 2000; Grunze Н., 2009; Malhi G., 2009; Leucht S„ 2009; Cipriani A., 2011).
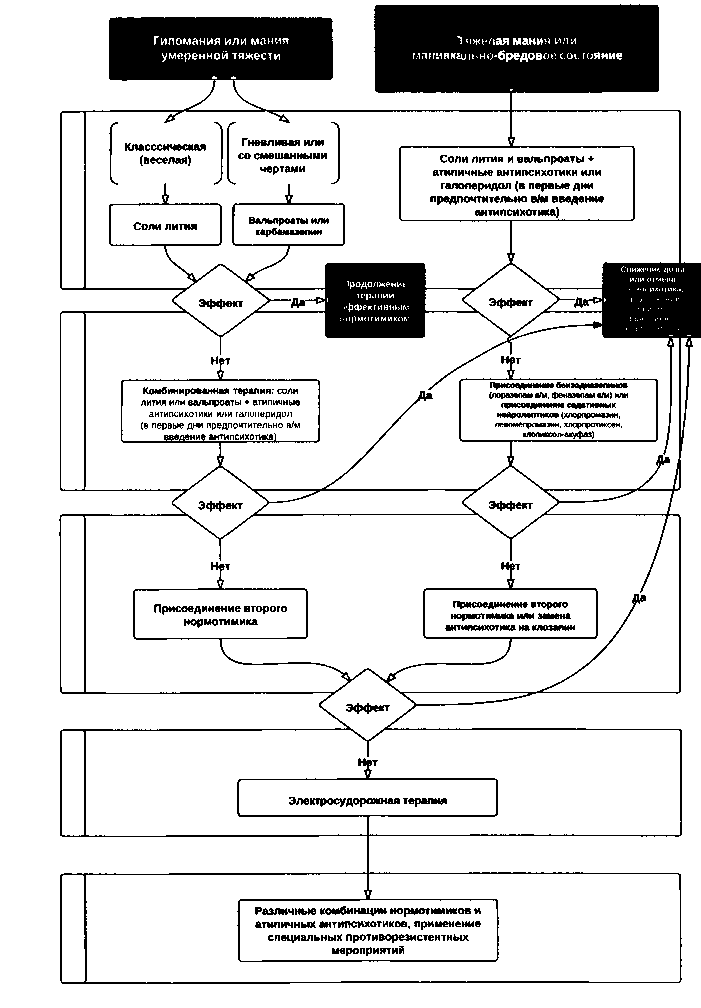
В целом, проведенные исследования подтвердили перспективность использования АА при терапии МС (отдельные препараты практически не отличаются по эффективности) и показали необходимость дополнительного изучения режима дозирования и оценки безопасности АА, а также возможности проведения длительной противорецидивной терапии у больных БАР. Кроме того, с целью уточнения места АА в системе принятой у нас в стране схемы антиманиакальной терапии представляется важным проведение отечественных сравнительных исследований, в том числе фармакоэкономических. Принимая во внимание вышеизложенные данные и собственный опыт клинических исследований, можно рекомендовать следующий ориентировочный алгоритм терапии МС, учитывающий их основные клинические формы и динамику состояния (рис. 2) (Мосолов С.Н., 2008).
Учитывая лучшую неврологическую переносимость, отсутствие депрессогенного действия, высокую эффективность при смешанных состояниях, АА в виде монотерапии или в комбинации с нормотимическими средствами могут быть рекомендованы в качестве препаратов первого выбора при купировании маниакальных и маниакальнобредовых состояний.
Литература
- Кузавкова М. В., Беленькая Д. В. Сравнительная клиническая эффективность кветиапина, оланзапина и рисперидона при купировании острых маниакальных состояний у больных с биполярным расстройством I типа//Х1У Съезд психиатров России (материалы съезда), 2005; 15-18 ноября, с. 274.
- Мосолов С. Н. Осложнения при сочетанном применении солей лития с нейролептиками у больных с эндогенными психозами//Журн. невропатол. и психиатрии им. С. С. Корсакова. -1983, Т. 83, № 3, с. 115-121.
- Мосолов С. Н. Дифференцированная терапия маниакальных, маниакально-бредовых и маниакально-гебефренных состояний при эндогенных психозах. Дисс. на соиск. учен. степ, канд. мед. наук. М., 1983, с. 239.
- Мосолов С. Н. Биполярное аффективное расстройство: диагностика и терапия. — М.: МЕДпресс-информ, 2008, с. 384.
- Шафаренко А. А., Капилетти С. Г., Мосолов С. Н. Сравнительная эффективность и переносимость атипичных антипсихотиков при купировании маниакальных состояний в рамках шизоаффективного и биполярного расстройств//Социальная и клиническая психиатрия, 2011, том 21, №3, с. 58-65.
- Ahlfors U.G., Baastrup Р.С., Dencker S.J. et al. Flupenthixol decanoate in recurrent manic-depressive illness. A comparison with lithium//Acta psychiatr. Scand., 1981, № 9; Vol. 64 (3): p. 226-37
- Baker R. W., Kinon B., Liu H., Schuh L., Bergstrom R., Hill A. Rapid initial dose escalation of oral olanzapine for acute agitation//Poster presentation, XHth World Congress of Psychiatry. 2002, Yokohama, Japan.
- Baldessarini R., Tarazi E Pharmacotherapy of psychosis and mania//In: Brunton L. L., LazoJ.S., Parker K.L. (eds). Goodman and Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 11th edn. McGraw-Hill Press: New York, 2005, p. 461-500.
- Berk M., Ichim L., Brook S. Olanzapine compared to lithium in mania: a double-blind randomized controlled trial//Inter. Clin. Psychopharmacology, 1999; № 14, p. 339-43.
- Bourin M. Aripiprazole: a viewpoint by Michel Bourin//CNS Drugs. 2004, Vol. 18 (№ 6): p. 377-378
- Bowden C., Sachs G. Treatment of acute mania with risperidone: focus on safety//Inter.J. N europsychopharmacology, 2000, V. 3, Suppl.l, p. 142-145
- recher M., Huizar K. Quetiapine vs placebo for acute mania associated with bipolar disorder//Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol., 2003, № 13, Suppl. 4: S 338, Abs p. 2.133.
- Brook S., Walden J., Benattia I., Siu C. O., Romano S.J. Ziprasidone and haloperidol in the treatment of acute exacerbation of schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder: comparison of intramuscular and oral formulations in a 6-week, randomized, blinded-assessment study//Psychopharmacology (Berl), 2005, № 178, p. 514-523.
- Brown E., Nejtek V., Perantie D. Quetiapine in bipolar disorder and cocaine dependence//Bipolar Disorder, 2002, V 4 (6), p. 406-411.
- Calabrese J., Stet L., Kotari H., et al. Asenapine as adjunctive treatment for bipolar mania: results of a placebo-controlled 12-week study and 40-week extension [abstract]//Proceedings of the 163rd Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association, 2010 May 22-26; New Orleans, LA. Red Hook, NY: Curran Associates.
- Calabrese J.R., Kimmel S. E., Woyshville M.J. et al. Clozapine for treatment refractory mania//Am. J. Psychiatry, 1996, № 153, p. 759-764.
- Canuso C., Zhu Y., Bossie C., Grossman F. Remission with risperidone in combination with mood stabilizers in acute bipolar mania//Ann. Meeting, American Psychiatric Association, San Francisco, California, USA, May 17-22, 2003. Abstracts NR: 188.
- Carson W., Sachs G., Sanchez R., et al. Aripiprazole vs placebo for the treatment of acute mania in patients with bipolar I disorder//Inter.J. Neuropsychopharmacology, 2004, № 7 (Suppl.l), p. 242.
- Cavazzoni P. A., Berg P. H., Kryzhanovskaya L. A., Briggs S. D., et al. Comparison of treatment-emergent extrapyramidal symptoms in patients with bipolar mania or schizophrenia during olanzapine clinical lrials//Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 2006, № 67, p. 107-113.
- Centorrino F., Meyers A., Ahl J., Cincotta S., Zun L. An observational study of the effectiveness and safety of intramuscular olanzapine in the treatment of acute agitation in patients with bipolar mania or schizophrenia/schizoaffective disorder//Hum. Psychopharmacol., 2007, Aug, 21.
- Cipriani A., Barbui C., Salanti G., Rendell J., Brown R, Stockton S., Purgato M., Spineli L.M., Goodwin G. M., Geddes J. R. Comparative efficacy and acceptability of antimanic drugs in acute mania: a multiple-treatments meta-analysis//Lancet, 2011, № 378 (9799), p. 1306-15, Epub 2011, Aug 16.
- ChouJ.C., ZitoJ.M., VitralJ., et al. Neuroleptics in acute mania: pharmacoepidemiologic study//Ann. Pharmacother., 1996; № 30, p. 1396-1398.
- Currier G. W., Citrome L. L., Zimbroff D. L., Oren D., Manos G., McQuade R. Intramuscular aripiprazole in the control of agitation//J. Psychiatr. Pract, 2007, № 13 (3), p. 159-169.
- Cutler A., Datto C., Nordenhem A., Minkwitz M., Acevedo L., Darko D. Extended-Release Quetiapine as Monotherapy for the Treatment of Adults With Acute Mania: A Randomized, Double-Blind, 3-Week Trial//Clinical Therapeutics, 2011, Vol. 33, № 11, p. 1643-1658.
- Daniel D. G., Potkin S.G., Reeves K. R., et al. Intramuscular (IM) ziprasidone 20 mg is effective in reducing acute agitation associated with psychosis: a double-blind, randomized trial//Psychopharmacology, 2001, № 155, p. 128-34.
- Daniel D. G., Brooke S., Warrington L. E., et al. IM ziprasidone in agitated patients with bipolar diagnoses//Presented at National Institute of Mental Health, New Clinical Drug Evaluation Unit, 44th Annual Meeting, 2004, Pheonix, AZ.
- DelBello M. P, Schwiers M. L., Rosenberg H. L., Strakowski S. M. A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study of quetiapine as adjunctive treatment for adolescent mania//J. Am. Academy Child and Adolescent Psych., 2002; № 41 (10), p. 1216-23.
- Eerdekens M., Karcher K., Grossman F. Risperidone monotherapy in acute bipolar mania//Eur. Neuropsychopharmacology, 2003, № 13, Suppl. 4, p. 317-321
- Esparon J., Kolloori J., Naylor G., McHarg A., Smith A., Hopwood S. Comparison of the prophylactic action of flupenthixol with placebo in lithium treated manic-depressive patients//Br.J. Psychiatry, 1986, № 148, p. 723-5.
- Figueroa C., Brecher M., Hamer-Maansson J., Winter H. Pharmacokinetic profiles of extended release quetiapine fumarate compared with quetiapine immediate release//Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry, 2009, № 33, p. 199-204.
- Focas C., Vartzopoulos D. Open — label risperidone in acute bipolar mania//Poster presentation XHth World Congress of Psychiatry, 2002, Yokohama, Japan.
- Frazier J. A., BiedermanJ., Jacobs T.G. et al. A prospective open-label treatment trial of olanzapine monotherapy children and adolescents with bipolar disorder//J. Am. Academy Child and Adolescent Psych., 2001, Vol. 11 (3), p. 259-262.
- Ghaemi S., Goldberg J., Ко J., McNally E. Quetiapine treatment of rapid-cycling bipolar disorder: An open prospective study//Eur. Neuropsychopharmacology, 2002, Suppl. 3, S 219.
- Gonzalez J., Thompson P., Moore T. Review of the safety, efficacy, and side effect profile of asenapine in the treatment of bipolar 1 disorder//Patient Prefer Adherence, 2011, № 5, p. 333-41. Epub 2011 Jul. 1.
- Goodwin EK., Jamison K. R. Manic-Depressive Illness//Oxford University Press, New York, 1990. P. 369-596.
- Grunze H., Vieta E., Goodwin G.M., Bowden C., Licht R.W., Moller H.J., Kasper S. The World Federation of Societies of Biological Psychiatry (WFSBP) guidelines for the biological treatment of bipolar disorders: update 2009 on the treatment of acute mania//World Journal of Biological Psychiatry, 2009, № 10, p. 85-116.
- Hirschfeld R., Keck P, Kramer M., Grossman F Rapid antimanic effect of risperidone monotherapy. A 3-week multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial//Bipolar Disorder, 2003, Vol. 5, Suppl. 1 P. 36.
- Hirschferld R. M., Calabrese J. R., Weissman M. M. et al. Sreening for bipolar disorder in the community//J. Clin. Psychiatry. 2003; 64:53-59.
- Jones M., Huizar K. Quetiapine monotherapy for acute mania associated with bipolar disorder//Inter.J. Psychiatry Clinical Practice, 2003, № 7 (4): 310-1, Abs P. 14
- Kane J., Barrett E., Casey D. et al. Metabolic effects of treatment with atypical antipsychotics//J. Clin. Psychiatry. 2004. Vol. 65. P. 1447-1455.
- Kay S. R., Fizbein A., Opler L. A. The Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) for schizophrenia//Schizophrenia Bulletin, 1987; № 13, P.1987-1276.
- Keck P., Calabrese J. R., McQuade R. D., Carson W. H., Carlson B.X., Rollin L. M., Marcus R.N., Sanchez R.; Aripiprazoie Study Group. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled 26-week trial of aripiprazoie in recently manic patients with bipolar I disorder//J. Clin. Psychiatry, 2006, № 67 (4), p. 626-37.
- Keck P, Marcus R., Tourkodimitris S. et al. A placebo-controlled, double-blind study of the efficacy and safety of aripiprazoie in patients with acute bipolar mania//Am.J. Psychiatry, 2003, №160, p. 1651-1658.
- Keck P, Versiani M., Potkin S. et al. Ziprazidone in the treatment of acute bipolar mania: a three-week, double blind, placebo-controlled randomized trial//Am. J. Psychiatry, 2003, № 160, 741-748.
- Khanna S., Vieta E., Lyons B. et al. Risperidone monoterapy in acute bipolar mania//Bipolar Disorder, 2003, Vol. 5, Suppl. 1, p. 60
- King K. G., David S. R., Beasley С. M., Alaka K. QTc interval profile of IM olanzapine in acute agitation//Poster Presentation at the XHth World Congress of Psychiatry, 2002, Yokohama, Japan.
- Kupfer D.J., Frank E., Grochocinski V.J., Luther J. F. Stabilization in the treatment of mania, depression and mixed states//Acta Neuropsychiatry, 2000, № 12, p. 110-114.
- Leucht S., Arbter D., Engel R. R., Kissling W., Davis J. M. How effective are second-generation antipsychotic drugs? A meta-analysis of placebo-controlled trials//Mol. Psychiatry, 2009, № 14, p. 429-447.
- Malhi G., Adams D., Lampe L., Paton M., O’Connor, Newton L. A., Walter G., Taylor A., Porter R., Mulder R. T, Berk M. Clinical practice recommendations for bipolar disorder//Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica, 2009, № 439, p. 27-46.
- Marcus R., Khan A., Rollin L., et al. Efficacy of aripiprazoie adjunctive to lithium or valproate in the long-term treatment of patients with bipolar I disorder with an inadequate response to lithium or valproate monotherapy: multicenter, double-blind, randomized study//Bipolar Disord., 2011, №13(2), p. 133-144.
- Masi G., Mucci M., Millepiedi S. Clozapine in adolescent inpatients with acute mania//J. Child Adolesc. Psychopharmacol., 2002; № 12 (2), p. 93-99.
- McElroy S. L., Dessain E. S., Pope H.G.et al. Clozapine in the treatment of psychotic mood disorders, schizoaffective disorder, and schizophrenia//J. Clin. Psychiatry, 1991; № 52, p. 411-414.
- McIntyre R. S., Cohen M., ZhaoJ., Alphs L., Macek T. A., PanagidesJ. Asenapine in the treatment of acute mania in bipolar I disorder: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial//J. Affect. Disord., 2010, № 122, p. 27-38.
- McIntyre R.S., Cohen M., ZhaoJ., Alphs L., Macek T. A., PanagidesJ. Asenapine for longterm treatment of bipolar disorder: a double-blind 40-week extension study//J. Affect. Disord., 2010, № 126, p. 358-365.
- McIntyre R. S., Cohen M., ZhaoJ., Alphs L., Macek T. A., PanagidesJ. Asenapine versus olanzapine in acute mania: a double-blind extension study//Bipolar Disord., 2009, № 11, p. 815-826.
- McIntyre R. S., Brecher M., Paulsson B. et al. Quetiapine or haloperidol as monotherapy for bipolar mania — a 12-week, double-blind, randomized, parallelgroup, placebo-controlled trial//Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol., 2005, № 15, p. 573-585.
- Meehan K., Zhang E, David S. et al. A double blind, randomized comparison of the efficacy and safety of intramuscular injections of olanzapine, lorazepam, or placebo in treating acutely agitated patients diagnosed with bipolar mania//J. Clin Psychopharmacol, 2001, № 21, p. 389-397.
- Meltzer H. Atypical antipsychotic drugs in the treatment of Bipolar Affective Disorder//Poster presentation, XXIst C. I.N. P. Congress, 1998, Glasgow, UK.
- Meulien D., Huizar K., Brecher M. Safety and tolerability of once-daily extended release quetiapine fumarate in acute schizophrenia: pooled data from randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies//Hum. Psychopharmacol., 2010, Vol. 25, p. 103-115.
- Montgomery S. A., Asberg M. A new depression scale designed to be sensitive to change//Br.J. Psychiatry, 1979, № 134, P. 382-389.
- Mukherjee S., Rosen A., Caracci G., Shukla S. Persistent tardive dyskinesia in bipolar patients//Archives of General Psychiatry, 1986, № 43, p. 342-346.
- Mullen J., Paullson B., Sweitzer D. Quetiapine in combination with mood stabilizer for the treatment of acute mania associated with bipolar disorder//Int.J. Psych. Clin. Practic, 2003, № 7 (4): 311-2, Absp. 17.
- Niufan G., Tohen M., Qiuqing A., Fude Y. et al. Olanzapine versus lithium in the acute treatment of bipolar mania: a double-blind, randomized, controlled trial//Journal of Affective Disorders, 2008, № 105, p. 101-118.
- Overall J.E., Gorham DR. The Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale//Psychological Reports, 1962; № 10, p. 799-812.
- Paulsson B., Huizar K. Quetiapine monotherapy vs placebo for acute mania//Bipolar Disorder, 2003, Vol. 5, Suppl. 1, p. 74.
- Perlis R. H., Baker R. W., Zarate C. A. Jr., Brown E.B., et al. Olanzapine versus risperidone in the treatment of manic or mixed States in bipolar I disorder: a randomized, double-blind trial//Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 2006, № 67, p. 1747-1753.
- Petty E, Sachs G., Bowden C. Efficacy of risperidone in psychotic and non-psychotic patients with bipolar disorder//Inter.J. Neuropsychopharmacol., 2000, Vol 3, № 7, Suppl. 1, p. 142.
- Preval H., Klotz S.G., Southard R., et al. Rapid-acting IM ziprasidone in a psychiatric emergency service: a naturalistic study//General Hospital Psychiatry, 2005, № 27, p. 140-144.
- Rosa A., Reinares M., Franco C., Comes M., Torrent C., Sanchez-Moreno J., Martinez-Aran A., Salamero M., Kapczinski E, Vieta E. Clinical predictors of functional outcome of bipolar patients in remission//Bipolar Disorders, 2005, № 11, p. 401-409.
- Sachs G. S., Gaulin B. D., Gutierrez-Esteinou R., McQuade R. D., Pikalov A. 3rd, Pultz J. A., Sanchez R., Marcus R.N., Crandall D.T. Antimanic response to aripiprazole in bipolar I disorder patients is independent of the agitation level at baseline//J. Clin. Psychiat., 2007, № 12, p. 1148-1155.
- Sachs G., Sanchez R., et al. Aripiprazol in the treatment of acute manic or mixed episodes in patients with bipolar I disorder: a 3-week placebo-controlled study//J. Psychopharmacol, 2006, № 68 (9), p. 1377-1383.
- Sachs G., Chengappa K., Suppes T. et al. Quetiapine with lithium or divalproex for the treatment of bipolar mania: a randomised, double — blind, placebo-controlled study//Bipolar Disorder, 2004, Vol. 6, p. 213-223.
- Sachs G., Grossman E, Ghaemi S. Combination of a mood stabilizer with risperidone or haloperidol for treatment of acute mania: double — blind, placebo-controlled comparison of efficacy and safety//Am. J. Psychiatry, 2002, № 7, p. 1146-1154.
- .Sachs G., Printz D., Kahn D. et al. The Expert Consensus Guideline Series: Medication Treatment of Bipolar Disorder, 2000. Postgrad. Med., № 4, p. 1-104.
- Sanchez-Moreno J., Martinez-Aran A., Tabares-Seisdedos R., Torrent C., Vieta E., Ayuso-MateosJ.L. Functioning and disability in bipolar disorder: an extensive review//Psychotherapy and Psychosomatics, 2009, № 78, p. 285-297.
- Segal S., Riesenberg R., Ice K., English P Ziprasidone in mania: A 21-day randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial//Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol., 2003, № 13, Suppl. 4, p. 345.
- Sierra P, Livianos L., Rojo L. Quality of life for patients with bipolar disorder: relationship with clinical and demographic variables//Bipolar Disorders, 2005, № 7, p. 159-165.
- Smulevich A. B., Khanna S., Eerdekens M., Karcher K., Kramer M., Grossman F. Acute and continuation risperidone monotherapy in bipolar mania: a 3-week placebo-controlled trial followed by a 9-week double-blind trial of risperidone and haloperidol//Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol., 2005, № 15, p. 75-84.
- 79.Suppes T., Webb A., Paul B. et al. Clinical outcome in a randomized 1-year trial of clozapine vs treatment as usual for patients with treatment-resistant illness and a history of mania//Amer.J. Psychiat., 1999; № 156; P. 1164-1169.
- Tohen M., Vieta E., Goodwin G.M., Sun B., et al. Olanzapine versus divalproex versus placebo in the treatment of mild to moderate mania: a randomized, 12-week, double-blind study//Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 2008, № 69, p. 1776-1789.
- Tohen M., Kryzhanovskaya L., Carlson G., DelBello M., et al. Olanzapine versus placebo in the treatment of adolescents with bipolar mania//American Journal of Psychiatry, 2007, № 164, p. 1547-1556.
- Tohen M., Goldberg J. E, Gonzalez-Pinto A. M., Azorin J. M., et al. A 12-week, double-blind comparison of olanzapine vs haloperidol in the treatment of acute mania//Archives of General Psychiatry, 2003a, № 60, P1218-1226.
- Tohen M., Baker R. W., Altshuler L. L. et al. Olanzapine versus divalproex in the treatment of acute mania//Amer.J. Psychiat., 2002, № 159, p. 1011-1017.
- Tohen M., Chengappa K.N.R., Suppes T. et al. Efficacy of olanzapine in combination with valproate or lithium in the treatment of mania in patients partially nonresponsive to valproate or lithium monotherapy//Archiv. Gen. Psychiat., 2002; № 59, P.62-69.
- Tohen M, Jacobs T. G., Grundy S.L et al. Efficacy of olanzapine in acute bipolar mania: A double-blind, placebo-controlled study//Archiv. Gen. Psychiat., 2000; № 57, P.841-849.
- Tohen M., Sanger T. M., McElroy S. L. et al. Olanzapine versus placebo in the treatment of acute mania//Amer.J. Psychiat., 1999; № 156; P. 702-709.
- Tohen M., Zhang E, Taylor C., Burns P, et al. A meta-analysis of the use of typical antipsychotic agents in bipolar disorder//Journal of Affective Disorders, 2001, № 65, p. 85-93.
- Tohen M., Zhang E, Keck P. E. et al. Olanzapine versus haloperidol in schizoaffective disorder, bipolar type//J. Affect.Disorder, 2001; № 67, P133-140.
- Velligan D., Weiden P., Sajatovic M. et al. Strategies for addressing adherence problems in patients with serious and persistent mental illness: recommendations from the expert consensus guidelines//J. Psychiatr. Pract., 2010, № 16, p. 306-324.
- Vestergaard P. Treatment and prevention of mania: a Scandinavian perspective//Neuropsychopharmacology, 1992; № 7, p. 249-259.
- Vieta E., Ramey T., Keller D., English R, Loebel A., Miceli J. Ziprasidone in the treatment of acute mania: a 12-week, placebo-controlled, haloperidol-referenced study//J. Psychopharmacol., 2010, № 24 (4), p. 547-58, Epub 2008, Dec 12.
- Vieta E., Owen R., Baudelet C., McQuade R.D., Sanchez R., Marcus R.N. Assessment of safety, tolerability and effectiveness of adjunctive aripiprazole to lithium/valproate in bipolar mania: a 46 week, open label extension following a 6 week double blind study//Curr. Med. Res. Opin., 2010, №26 (6), p. 1485-149.
- Vieta E., Tohen C., McQuade R. D., et al. Adjunctive aripiprazole in bipolar mania partially non-responsive to valproate/lithium: a placebo-controlled study//Am.J. Psych., 2008, № 165, p. 1316-25.
- Vieta E., Bourin M., Sanchez R. et al. Effectivness of aripiprazol vs haloperidol in acute bipolar mania: double-blind, randomized, comparative 12-week trial//Brit. J. Psychiat., 2005, № 187, p. 235-242.
- Vieta E. Quetiapine in the treatment of rapid cycling bipolar disorder//Bipolar Disorder, 2002, Vol. 4 (№ 5), p. 335-340.
- Vieta E. Corbella B., Benabarre A. et al. Treatment of mixed mania with adjunctive risperidone//Inter.J. Neuropsychopharmacology, 2000, V. 3, № 7, Suppl. 1, p. 143.
- Weisler R., Dunn J., English P. Ziprasidone in adjunctive treatment of acute bipolar mania: randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial//Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol., 2003, № 13, Suppl.4, p. 344.
- Yatham L., Grossman E, Augustyns I., Vieta E. Mood stabilizers plus risperidone or placebo in the treatment of acute mania. International, double blind, randomized controlled trial//Brit.J. Psychiat., 2003, № 182, p. 213-223.
- Young A., Oren D., Lowy A., McQuade R., Marcus R., Carson W., Spiller N., Torbeyns A., Sanchez R. Aripiprazole monotherapy in acute mania: 12-week randomized placebo- and haloperidol-controlled study//Br. J. Psychiatry., 2009, № 194 (1), p. 40-8.
- Young R. C., Briggs J.T., Ziegler V. E., Meyer D. A. A rating scale for mania reliability, validity and sensitiyity//Brit.J. Psychiat., 1978; № 133, P.429-435.
- Zajecka J., Weisler R., Sachs G. et al. A comparison of the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of divalproex sodium and olanzapine in the treatment of bipolar disorder//J. Clin. Psychiat., 2002, №12, p. 1148-1155.
- Zarate C. Jr., Tohen M. Double-blind comparison of the continued use of antipsychotic treatment versus its discontinuation in remitted manic patients//American Journal of Psychiatry, 2004, № 161, p. 169-171.
- Zimbroff D. L., Marcus R. N., Manos G., Stock E., McQuade R. D., Auby P, Oren D. A. Management of acute agitation in patients with bipolar disorder: efficacy and safety of intramuscular aripiprazole//J. Psychopharmacol, 2007, № 27 (2), p. 171-176.